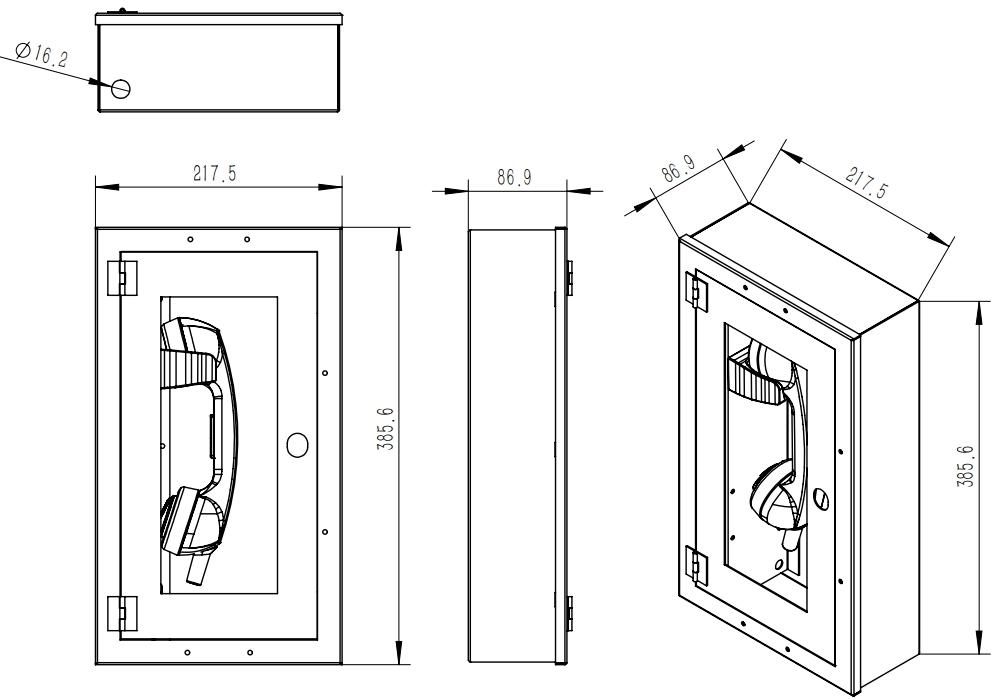
High-rise fires create dangerous situations where clear communication saves lives. Emergency Voice Communication Systems Fire Telephone, like the Joiwo JWAT162-2, ensures that emergency teams and building occupants stay connected. Tipo de telefone de incêndio Externos e o auto dial emergency telephone offer reliable, direct support when every second counts.
Communication Challenges in High-Rise Fires

Noise, Confusion, and Environmental Hazards
High-rise fires create chaotic environments. Loud alarms, shouting, and the roar of flames make it hard for people to hear instructions. Many occupants struggle to recognize fire alarms, especially if they have experienced false alarms before. Some may hesitate or ignore warnings, delaying evacuation. Environmental hazards such as smoke, hazardous materials, and damaged infrastructure add to the confusion. Stress and fear can cloud judgment, making it even harder to follow directions. Disrupted services like water and electricity further complicate communication and safe movement.
- Noise and confusion reduce the effectiveness of emergency cues.
- Occupants may not trust alarms due to past false alarms.
- Environmental hazards and damaged infrastructure create ongoing stress.
- Psychological effects, such as fear and trauma, impact decision-making.
Power Outages and System Failures
Power outages often occur during major fires. These outages can knock out communication systems, making it difficult for emergency teams to coordinate. In past disasters, such as the collapse of WTC building 7, loss of power led to the failure of telephone lines and mobile networks. Emergency responders struggled to communicate, and critical warnings did not reach those in danger. Backup systems sometimes fail, leaving teams to rely on temporary solutions like mobile towers or satellite phones.
- Power loss disrupts both wired and wireless communication.
- Emergency command centers may lose contact with field teams.
- Temporary solutions help but may not cover all needs.
Building Size and Structural Complexity
Large high-rise buildings present unique challenges. Their height and complex systems create many pathways for fire and smoke. Firefighters may have trouble reaching upper floors quickly. Elevators, ventilation, and alarms can fail, making communication harder. High occupant numbers require careful coordination. Phased evacuations mean only certain floors move at a time, so real-time, zone-specific instructions become vital. Without reliable communication systems, evacuation plans can break down under stress. Voice alarm systems and bidirectional amplifiers help, but they need careful design and regular testing to work well in these complex environments.
Emergency Voice Communication Systems Fire Telephone Solutions

Reliable Two-Way Communication in Critical Areas
Emergency Voice Communication Systems Fire Telephone play a vital role in high-rise fire safety. These systems provide a direct link between fire officers and control rooms, even when radio signals fail. The Joiwo JWAT162-2 stands out for its robust design and reliable performance. It uses a fixed, secure, bi-directional, full-duplex voice communication system. This setup ensures clear conversations in both directions, which is critical during emergencies.
The system features a durable red steel enclosure and a rugged handset. A push-to-open door protects the handset from damage and unauthorized use. The auto dial call function allows quick connection, saving valuable time. The device can be mounted on different surfaces, making it suitable for various building layouts. Its waterproof rating (IP65) and wide operating temperature range ensure it works in harsh conditions. The system supports communication in high humidity and extreme temperatures, which often occur during fires.
Note: Emergency Voice Communication Systems Fire Telephone enable targeted messaging to specific zones. This feature helps emergency teams give clear instructions to people in different parts of the building.
Key features include:
- Full-duplex voice communication for real-time updates.
- Rugged construction for physical protection.
- Auto dial for fast emergency response.
- Flexible installation options.
- Locking mechanism for security.
- Reliable operation in extreme environments.
These features help maintain communication when other systems fail. They support coordinated evacuations and improve life safety by delivering clear, location-specific instructions.
Step-by-Step Use and Maintenance of Fire Telephone Systems
Proper use and maintenance keep Emergency Voice Communication Systems Fire Telephone ready for action. Building staff and emergency teams should follow a clear process to ensure system reliability.
Using the System:
- Locate the fire telephone outstation, usually near entrances or firefighting lobbies.
- Open the push-to-open door and lift the handset.
- Wait for the control room operator to answer.
- Communicate the situation clearly, stating location and needs.
- Follow instructions from the control room.
Maintaining the System:
- Perform visual inspections of all components weekly.
- Test batteries monthly or bi-monthly, depending on type.
- Check detectors and control equipment semiannually and annually.
- Test alarm notification appliances both visually and audibly.
- Replace power supplies as needed to keep the system operational.
- Restore systems promptly after any test or alarm.
- Keep spare devices and components available for quick repairs.
- Ensure only trained personnel perform maintenance and testing.
A regular maintenance schedule follows industry standards such as OSHA and NFPA 72. These protocols require bi-monthly testing of non-supervised systems and annual testing of supervised systems. All manual actuation devices must remain unobstructed and accessible.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Responsible Party |
|---|---|---|
| Visual inspection | Semanalmente | Trained personnel |
| Battery check | Monthly/Bi-monthly | Trained personnel |
| Detector and control equipment | Semiannual/Annual | Trained personnel |
| Alarm appliance test | Quarterly/Annual | Trained personnel |
| Power supply replacement | Conforme necessário | Trained personnel |
Best Practices for Integration and Training
Integrating Emergency Voice Communication Systems Fire Telephone with other building safety systems increases overall effectiveness. Early planning ensures cable routes and equipment locations fit the building design. Compliance with local codes and standards, such as NFPA 72 and OSHA, is essential. Annual inspections and maintenance keep systems reliable.
Certified installers and engineers should handle system design, installation, and testing. NICET Level III certification demonstrates advanced knowledge and skill. Proper documentation supports future upgrades and ensures system security.
Tip: Integrate voice evacuation systems with building automation and access control. This allows centralized management and automated emergency responses.
Training is key to effective use. Emergency staff and building occupants should participate in regular drills. These drills teach people how to use the fire telephone, recognize voice alerts, and follow evacuation instructions. Staff should explain the system’s capabilities and demonstrate the location and operation of manual pull stations and warden phones. Occupants must know to listen for voice announcements and follow staged evacuation instructions.
Best practices include:
- Early involvement in system planning and design.
- Compliance with Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) requirements.
- Annual inspections and maintenance.
- Use of certified professionals for installation and testing.
- Thorough system testing and commissioning.
- Planning for future building developments and system expansion.
- Integration with building automation for centralized control.
- Regular training and fire drills for staff and occupants.
These steps ensure Emergency Voice Communication Systems Fire Telephone remain reliable and effective, supporting clear communication and safe evacuation during high-rise fire emergencies.
Emergency Voice Communication Systems Fire Telephone, such as the Joiwo JWAT162-2, help building managers protect lives and property. Regular testing and training improve system reliability and reduce evacuation times. Clear voice messages support safe evacuations and minimize panic. Building managers should prioritize installation, maintenance, and staff training.
FAQ
What makes the Joiwo JWAT162-2 suitable for high-rise buildings?
The Joiwo JWAT162-2 offers reliable two-way communication, rugged construction, and waterproof protection. Firefighters and building staff can depend on it during emergencies.
How often should building staff test the fire telephone system?
Building staff should test the system at least once a month. Regular checks help ensure the system works when needed most.
Can the fire telephone system operate during power outages?
The system uses backup power sources. It continues to function even if the main power fails during a fire emergency.


